Nov 23, 2020 • Filed to: Answer Hard Drive Problems • Proven solutions
Free Download and information on Fat32format - FAT32format is able to easily format large hard disks in FAT32, even in Windows XP. FAT32format is a small, simple and strong software that canformat large hard disks in FAT32, even in Windows. Mac users should have it much easier! Start by opening the Disk Utility and selecting the SD card: Then hit the “Erase” button up top and select “MS DOS (FAT)” from the drop-down menu: Hit Okay and that should be it!: Now, I’m far from a Mac expert, but these screenshots were provided by Ray Commend, who tested and verified on his. FAT32format, free download. Format partition software for Windows: Creates FAT32-formatted drives including HDD, SDD, SD and memory cards. Review of FAT32format. Includes tests and PC download for 32-bit/64-bit systems. Como Formatar HD Externo ou Pendrive para FAT32 com guiformatPrograma No meu Blog Link http://evassmat.com/ZEL5.
If you also own a Linux system, which is running on low disk space, then you might be facing a similar situation. Although Linux is one of the most popular open-source operating systems, it can be a bit complicated at times. For instance, there is no direct solution to do a Linux format disk using a dedicated GUI feature. Don't worry – you can still erase disk on Linux with the help of the right commands. Read on and clear your Linux disk space by following this extensive guide.
Content
Part 1: Why We Need to Format and Wipe Linux Disk?
Before we get to know different ways to format a disk on Linux, it is vital to understand the reasons behind it. Ideally, there could be the following major reasons for wiping or formatting a disk on a Linux system:
- If your system is running low on free space, then you can choose to wipe the data of a partition or a disk.
- Sometimes, a system can become slow by having limited free space. By formatting its Linux drive, you can improve its performance as well.
- If your system has been corrupted by malware, then you can wipe the hard disk of your Linux to resolve this.
- Mostly, users prefer to do a Linux format disk before reselling their systems. This helps them protect their data.
- There could be an issue with the firmware or the system storage, which can be fixed after wiping a Linux disk.
Part 2: How to Format a Linux Hard Drive?
Guiformat X64
Unlike Windows or macOS, there is not a dedicated disk management tool that can help us partition or format the disk. Therefore, we need to take the assistance of certain commands to format a Linux disk. If you are connecting your drive for the first time to your Linux system, then you need to create a partition beforehand. To implement this, you can enter the fdisk command. Once a partition is created, you can use the 'mkfs.ext4' command to format the disk. Here's a simple solution to format a disk on a Linux system.
Step 1: Create a partition of the disk
Firstly, connect the disk to your Linux system if you haven't already and launch the Terminal window on it. You can enter the following command to check it:

sudo fdisk –l.
Now, to create a partition, enter the command 'fdsk' in the following format:
sudo fdisk /dev/sdb.
Gui Format Ridgecrop
This will launch the results of the fdisk command. If you want, you can type 'm' to get help. It will display a list of the supported parameters. You can type 'n' to create a new partition, 'd' to delete the partition, 'p' to check the partition table, and so on.
Firstly, press 'p' and enter to view the partition table. This will let you know about the disk identifier and the sector space. Subsequently, enter the 'n' command to create a new partition. You will be given an option to create a primary or an extended partition. Press 'p' to create a new primary partition and give it a number from 1 to 4. If you want to create a single partition, then enter '1'.
Step 2: Format the disk
Great! Once you have created the relevant partition on your Linux system, you can format it by entering the command –
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb.
This will make the system look for the available partitions on the drive. When you are asked to confirm your choice, just press 'y'. Afterward, wait for a while as the selected partitions would be formatted on the Linux system.
Step 3: Mount the file system (optional)
If you want, you can mount the file system as well. To do this, you can use the 'mkdir /data' command to make a directory. After that, end the following command to mount it:
mount /dev/sdb1 /data.
Part 3: How to Wipe a Hard Drive on Linux?
If you are planning to resell your system or are concerned about your privacy, then you should consider wiping the drive instead. Unlike formatting a disk, wiping it will erase the data and make the recovery process harder than before. Thankfully, there are multiple commands to do Linux wipe the disk. Here are some simple solutions to wipe a hard drive on Linux.
1. wipe
As the name suggests, the command is used to wipe data from a magnetic disk. Though, a lot of Linux systems do not have the command readily installed. In this case, you can use the apt install command first.
# apt install wipe.
Once it is done, just use the 'wipe' command in the format - wipe [options] target. For instance, to wipe a partition, simply enter the command:
# wipe /dev/sda2
Confirm your choice, by entering 'yes' and wait as the selected partition would be wiped.
2. shred
This is one of the best ways to protect your private data on a Linux system. Ideally, this works as a dedicated shredder – that would overwrite your data with something else, making the recovery process harder. This Linux based command has the following syntax:
shred [option] target
As you know, 'target' would specify the location you wish to shred. It can be a partition, folder, or file name. Subsequently, it can have the following options.
- -n: To overwrite data 'n' times
- -f: To change permission and allow the writing operation
- -u: Truncates the files after shredding them
- -s: To provide the size to shred
- -u: To remove the file after shredding
- -v: To enable the verbose mode
- -z: To add zeros to the final overwriting process
Gui Format Download For Mac
Therefore, you can wipe the Linux disk, by entering a command like this:
# shred -vfz -n 10 /dev/sda2.
This will follow ten passes of overwriting on the provided location, making it impossible for a recovery tool to retrieve data from it.
3. dd
If you are running short on time, then consider using the 'dd' command to erase disk on a Linux system. Instead of generating random data, it will overwrite the entire disk with strings of zeros. Therefore, it will take less time to wipe the disk and protecting your information. Although, it provides certain options that you can use to customize the process.
dd if=source of=target [Options].
Make sure that you run the command prompt and as a super-user. Here's a simple demonstration of the same.
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda2 bs=512 count=1.
The command will overwrite the target location with a string of zeros, as specified in the source. Also, this will copy 512 bytes in a single count. One of the major advantages of this is the time taken by the dd command is lesser than shred.
4. scrub
Lastly, you can also take the assistance of the 'scrub' command to overwrite your disk with specific patterns. Sometimes, the patterns can be randomly generated by the system too. Since the command is not present in every Linux system by default, you might need to install it first. To do this, you can use the apt install command.
Once it is done, just enter the command in the following syntax:
scrub [option] target.
Even if you don't provide an option and just specifies the target location to wipe, the command will work. Though, you would be asked to verify your choice to erase disk on Linux entirely. Here's a quick example of the same:
# scrub /dev/sda5.
Part 4: Tips for Formatting and Wiping Linux Disk
After getting to know about these popular commands to create new disk space on Linux, you would certainly be able to format or wipe it. Besides that, you can consider following these tips to format or wipe the Linux disk successfully.
- Make sure that you have logged-in as a super-user (administrator) while wiping a disk. This will make the entire process a whole lot easier.
- Not every command might be installed on your system. Therefore, you can consider checking its status or installing it beforehand.
- Although there are third-party applications available to shred and wipe a disk, it is recommended to use reliable commands. If you use a readily available tool, then make sure it is from a trusted source with a positive reputation in the industry.
- Always double-check the command before entering it (particularly the syntax and the location). One small error and you might end up causing irrevocable damage to your system.
- Most importantly, take a backup of your important files before wiping the Linux disk. This will make sure that you have a second copy of your vital data in advance.

That's a wrap, folks! Now when you know how to format or wipe disk on Linux, you can easily meet your requirements. In case if you have accidentally deleted your data or have formatted a drive, then use a reliable data recovery solution like Recoverit Data Recovery. Using it, you can just attach your Linux device to a PC and later extract the lost or inaccessible content from it. Go ahead and try some of these methods and feel free to share your shortcuts or tips in the comments below.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Data from Hard Disk After Disk Wipe
What's Wrong with Drive
- Recover Your Drive
- Fix Your Drive
- Format/Wipe Drive
- Know Your Drive
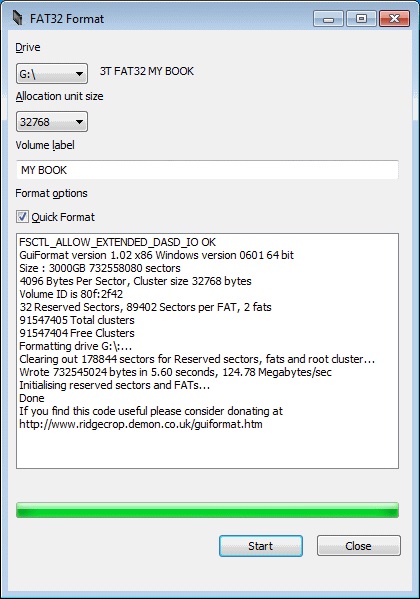
FAT32 Format is a simple, fast program for formatting hard drives and other storage media to the FAT32 format.
FAT32 Format is an aptly named tool that can format a storage device in the FAT32 file system. This version is designed specifically for the Windows 2000, XP, and Vista operating systems and will not work with newer versions, such as Windows 8, 8.1, and 10. The program is portable, which means that you can have it on your person on a USB flash drive or the like. It also doesn’t take up much space on a drive or require many resources during operation.
Be mindful that this is a Windows application rather than a program intended to run in DOS or from a command line interface. When you run the program, you’ll be presented with a minimalistic dialog window with just a few options. The drive will be set to C: by default, but you can choose another drive from the dropdown, which will be populated with all available drives. You can also dictate the allocation unit size in a similar manner. The default is fine in most cases, but if a drive needs a particular size for a particular purpose, this gives you that option.
When you’re ready to begin, click the Start button. The operation will then begin, and you’ll find that the process is relatively fast, but total time will depend greatly on the overall size of the drive being formatted. The main program window also has a text box that the program will use to post a progress report. If the operation fails for any reasons or errors are encountered, then the details of these problems will be reported here.
Pros
- Portable application
- Small footprint
- Fast, accurate process
Cons
- Only works with for Windows 2000, XP, and Vista